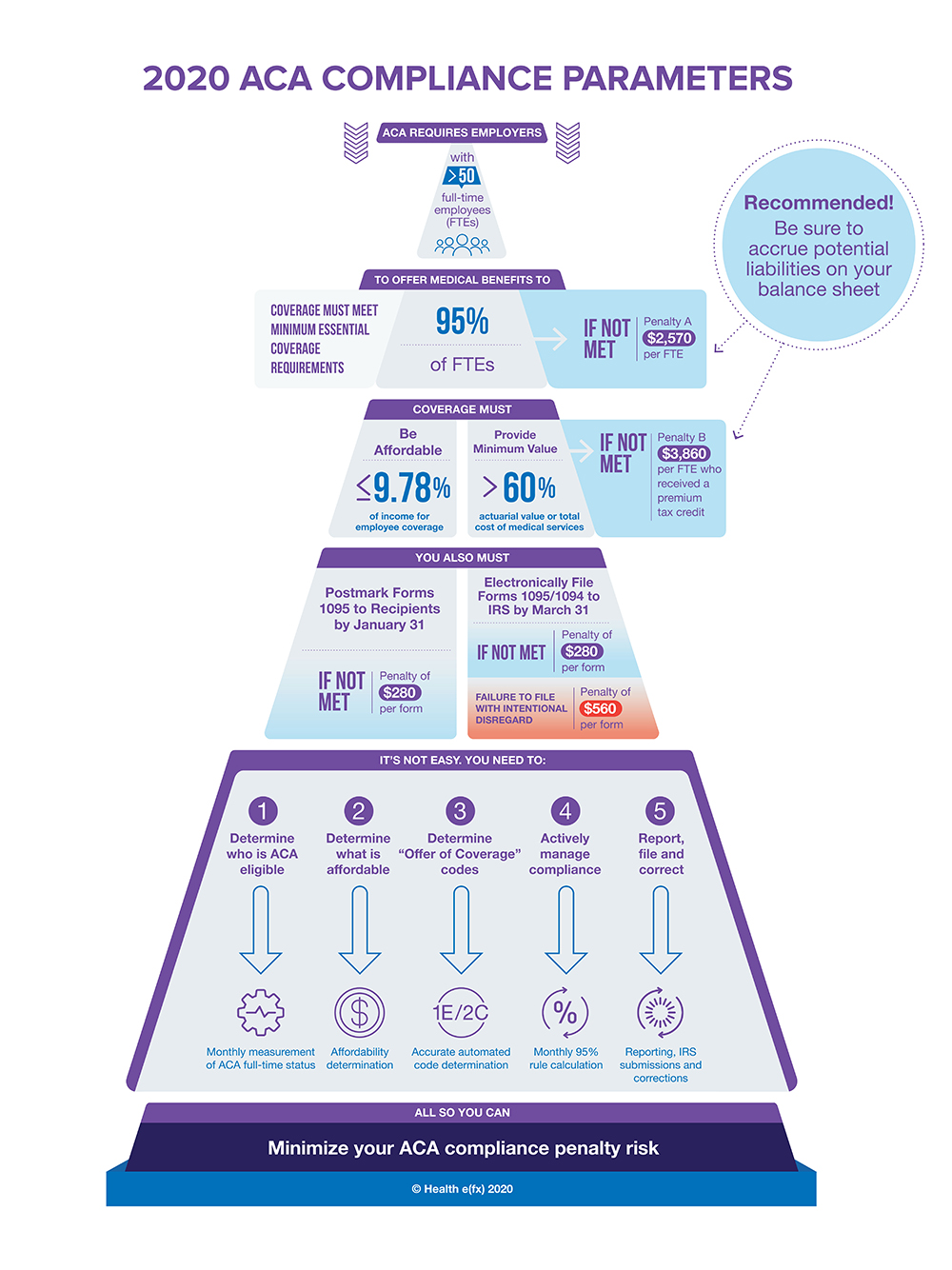
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires applicable large employers (ALEs) to offer 95% of their full-time employees healthcare coverage that meets minimum essential coverage requirements, provides minimum value (at least 60% actuarial value) and qualifies as affordable.
In tax year 2020, ALEs that fail to offer coverage to at least 95% of their employees could be deemed out of compliance by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and face fines of $2,570 per full-time employee (known as Penalty A).
Furthermore, failure to offer coverage that is judged affordable or provides minimum value can expose a company to Penalty B, with a fine of $3,860 for each employee who received a premium tax credit. These penalties accumulate monthly for each instance of noncompliance, which can cause penalty ramifications to grow quickly and substantially.
The infographic below, developed by Health e(fx), explains these ACA requirements and risks. For more details on ACA compliance, benefits, and workforce benchmarks and trends, read Health e(fx)’s latest 2020 Insights Report.